Hello, hope you are well. So now we will talk about pointers in C programming language. Today we talk about various sub topics of pointers are:- What is a pointer, Printing address present in pointer, Accessing a memory block with help of pointer, pointer to a pointer in c and Pointer to an Array. Read full article to better understanding, Lets start...
 |
| pointer in c |
Introduction of pointer in c:-
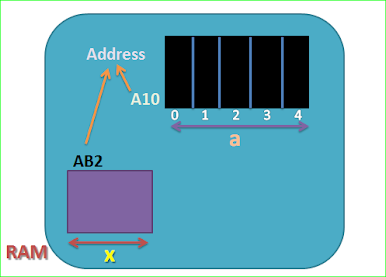
To store data, we can create a variable or we can create an array. A variable is of scalar type while an array is of aggregate type. Whenever an array or a variable is created, space is allocated in the memory(RAM).
For eg:-
int a[5]; //array
int x; //variable(scalar)
Each and every memory block which is created during the execution of a program is assigned a unique address automatically. The address in the hexadecimal format.
| 0 - 9 |
| A - 10 |
| B - 11 |
| C - 12 |
| D - 13 |
| E - 14 |
| F - 15 |
We can excess a memory block using its address. This is done using the concept of pointer.
Also Read: Control Statements In C - language
What is a pointer in c?
A pointer is a special variable which stores address of some another variables. To create a pointer variable, We use the following syntax:-
datatype * pointer var name;long * ptr;/*(here ptr is a pointer which can store address of any variable of long type only)*/pointer name=&variable name;int d;int *p;p=&d;C Printing address present in pointer
printf("%p",pointer var name);
//program using Printing address present in pointer
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
lang *ptr;
/*here ptr is a pointer which can stored address of any variable of type long.*/
long d;
clrscr();
ptr=&d;
/*the address of a variable 'd' have been stored in the pointer named ptr*/
printf("the address of d is %p",ptr);
/*here pointer named ptr is being printed. Whenevr a pointer is printed, the address in that pointer gets printed*/
getch();
} C Accessing a memory block with help of pointer
*pointer name;float *x;float a;a=90.8;x=&a;
//program Accessing a memory block with help of pointer
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
long *a;
long d=600000;
clrscr();
a=&d;
printf("the address of d is %p",a);
printf("\n the value at d is%ld",*a);
getch();
}
pointer to a pointer in c
Creating pointer to a pointer
datatype **pointer name;pointer to a pointer name = &pointer name;
//program Creating pointer to a pointer
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int x; //variable
int *a; //pointer
int **b; //pointer to a pointer
a=&x; /*address of x assigned to a pointer a*/
b=&a; /*address of pointer a assigned to pointer to pointer b*/
printf("the address of x is%p",a);
printf("\nthe address of a is%p",b);
getch();
}
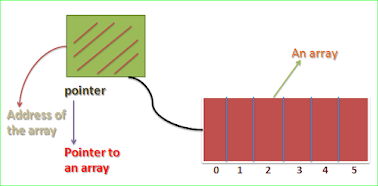
C Pointer to an Array
datatype *pointer name;float *b; /*here b is a pointer to an array of the float */1) pointer name=array name;
int *p;int a[5];p=a; //address of a assigned to p2)pointer=&array name[0];
int *ptr;int c[10];ptr=&c[0];
//program of pointer to an array
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int i;
int *p;
int a[10];
clrscr();
printf("enter 10 values\n");
for(i=0;i<=9;i=i+1)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
p=a;
/*address of a assigned to pointer p */
for(i=0;i<=9;i=i+1)
{
printf("%d",p[i]);
}
getch();
}



Comments
Post a Comment