What is String in C Language and String handling function
We are going on new topic of C language of String. If you are not read our previous topic. Then you can visit them and read it, for better understand. So, today we are talking about string , string handling functions and its types and declaring and initializing a string.
Char Datatype In C Language
 |
| Char Datatype In C Language |
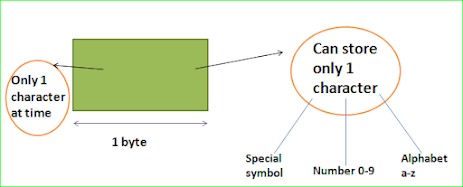
Whenever a variable of char type is created, It is allocated one byte of space in the memory. The Character assigned to a variable of type char, is assigned in single count.
syntax:
syntax:
char variable name;
Sample code:-
//program using char data type
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
char data;
clrscr();
printf("Enter a Character");
scanf("%c",&data);
printf("The character entered by user is %c",data);
getch();
}
String In C Language
Simple Definition of String:- To store more than one character, We use the concept of string. In C-Programming language, collection of character is referred to as string.
Some examples of strings that written like that is:-
A+, abc, 123, abc_xyz_123, a+, 3.14*r*r, a=l*b.
In C-language we create an array of type char to store a string.
Syntax:-
Syntax: datatype array name[size];
Example: Ex: char c[20];
To work on variable which is a string, We use '%s' (string). To fetch a string which contains whitespace(s), we use a special function named gets(string name).
Also Read: Control Statements In C - language
Scanf() is not able to save/store data with whitespace.
To work on string, we are provided with a header file named 'string.h'. This header file contains predefined methods for performing various operations on a string. Once a string has been created, we can perform operations such as concatenation, changing case of a string and copying a string into a another string.
Sample code:-
//A sample code of string.
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
void main()
{
char name[20];
clrscr();
printf("Enter your name");
gets(name);
printf("welcome %s",name);
getch();
} String handling function and its types in C Language
'string.h' contains the following functions which can be used to perform various types of operation on a string. These functions are called string handling functions.| 1) strlen() | 2) strcpy() | 3) strcat() |
| 4) strcmp() | 5) strupr() | 6) strlwr() |
| 7) strrev() |
Whenever a string is created, we can store characters in that string. The number of characters that can be stored in a string are equal to the size of the string.
Example:
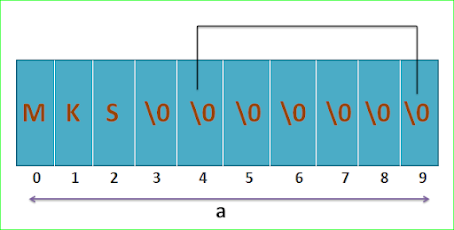
Ex: char a[10];If we store 'MKS' in storing named '0' then all the empty elements will be automatically filled by backselse '0' (\0) null character.
Also Read: Format Specifier In C Programming
1) strlen():-
strlen() is a string handling function which computes the length of a string. Strlen() counts the total number of characters present in a string/character array.
Strlen() starts counting the number of characters from the first element/first index number fill the null character (\0) is not encountered. It returns an integer value. That integer value is the length of the string.
Syntax:-
Syntax: integer var = strlen(string var name);Sample code:-//A program to fetch user name from the user. User name should be accepted if 10 character long or more, It should rejected otherwise..
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
void main()
{
int len;
char user[30];
clrscr();
printf("Enter your username");
gets(user); //gets will fetch the data entered by user.
len=strlen(user); /*strlen counts the total character in the string.*/
if(len<10 br="">
{
printf("username rejected");
}
else
{
printf("username accepted \n account created");
}
getch();
}
2)strcpy():-
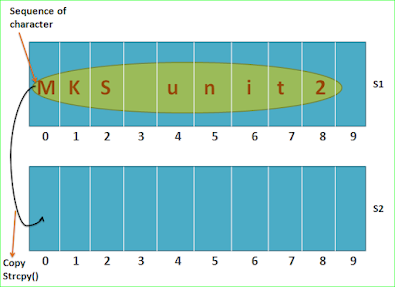
strcpy() is a method which is used to copy a sequence of character present in a string into another string.
 |
| strcpy() |
strcpy() is a string manipulation method which copies a string into another string.
Syntax:-
Syntax: strcpy(target string , source string);
Sample code:-
The size of the target string should be large enough to store the resultant string.
//A program to copying a string from one string to another string.
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
void main()
{
char s1[30];
char s2[30];
clrscr();
printf("enter a string");
gets(s1);
strcpy(s2,s1);
printf("data after copying\n");
printf("%s",&s2);
getch();
} 3) strcmp()
To compare two numeric values, we use == (comparison operator). == can't be used to check whether the two strings are identical or not.
To compare two strings, string.h header file provides strcmp() method. Strcmp() can be used to arrange string or to compare. strcmp() written an integer value.
Also Read: Variables & Datatypes In C Language
If zero is written, then it means that the two string are identical. If a negative value is written, then it means that the strings are in a shorted order. If positive value is written. Then it means that the two strings are not in shorted ordered.
Syntax:-
Syntax: integer var= strcmp(string1, string2);
Sample code:-//A program to compare two strings.
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
void main()
{
char s1[30];
char s2[30];
int i;
clrscr();
printf("enter 2 strings");
gets(s1);
gets(s2);
i=strcmp(s1,s2);
if(i==0)
{
printf("both strings are identical");
}
else if(i<0>)
{
printf("sorted order");
}
else
{
print("unsorted order");
}
getch();
}
4) strcat()
strcat() is a string manipulation function which is used to concatenate two strings. Strcat() adds a string in the end of another string.
Syntax:- Syntax: strcat(target, source);
Sample code:-
Strrev() is used when we want to check whether a given string is palindrome or not.
//A program to concatenate two strings.
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
void main()
{
char s1[20];
char s2[20];
clrscr();
printf("enter 1st name");
gets(s1);
printf("enter 2nd name");
gets(s2);
strcat(s1, s2);
printf("the concatenated data is:\n");
printf("%s",s1);
getch();
} 5) strupr()
Strupr() converts all the lower case character in a string into upper case character. Strupr() accepts the name of string as the arguments.
Syntax:-
Syntax: strupr(string);
Also Read: Format Specifier In C Programming .
Sample code:-//A program to convert lower case string into Upper case string.
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
void main()
{
char data[20];
clrscr();
printf("enter a string in lower case");
gets(data);
strupr(data);
printf("the data in upper case is\n");
printf("%s",data);
getch();
}
6) strlwr()
Strlwr() converts all the upper case character in a string into lower case character. Strlwr() accepts the name of string as the arguments.
Syntax:-
Syntax: strlwr(string);
Sample code:-//A program to convert Upper case string into lower case string.
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
void main()
{
char data[20];
clrscr();
printf("enter a string in upper case");
gets(data);
strlwr(data);
printf("the data in lower case is\n");
printf("%s",data);
getch();
}
7) strrev()
To reverse a string, string.h header file provides a method named strrev(). Strrev() reverses the character present in a string. It accepts name of the string as argument.
Syntax:-
Syntax: strrev(string);
Sample code:-
2). char name[size]="data";
We will going on series of C Programming language of all topics. So, you can follow us for more updates.
//A program to Reverse a string.
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
void main()
{
char s[30];
clrscr();
printf("enter a string");
gets(s);
strrev(s);
printf("The reversed data is");
printf("%s",s);
getch();
} How to declare and initializing string variables in C Language
A string is an array of type 'char'. A string is basically collection of character. To declare a string, we use the following syntax:-
Syntax: char name[size];
Their are various ways of creating and initializing string at the type of creation.
1). char name[ ]="data";
In this mechanism, the memory is allocated exactly according to the data the compiled calculates/computes the length of the string and then allocate the required amount of memory. In this mechanism their is no wastage of memory.
Also Read: Structure Of C Language Program .
For Ex:-
char s[ ]="c language";
In this mechanism their is wastage of memory if the number of characters in the string are less then the size of string. While declaring the string, we have to specify the size.
For Ex:-
char s[10]="loops";
3). char name[size]={' ',' ',' ',' ',' ','\0'};In this mechanism we have to specify the size of the array as well as the null character in the end of data. we specify a sequence of character.
For Ex:-
char s[6]={'s','a','y','e','d','\0'};





Comments
Post a Comment