Array in C Language Btech Bca Notes
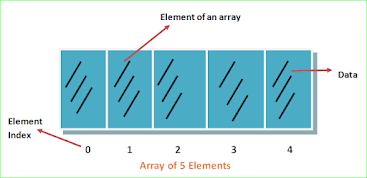
An array is a data form that can hold several values all of the same type. An array is a collection of variable of the same type that are referral to by a common name.
Also Read: Beginner our view on C programming Language .
Array are vital for most programming language. They are collection of variables, which we call elements.
Also Read: Beginner our view on C programming Language .
Array are vital for most programming language. They are collection of variables, which we call elements.
Each of the element in an array is stored sequentially in the computeric memory. This making it easy to manipulate them and navigate among them.
Since all the elements in an array are of same type, array allows us to represent a group of similar elements as an ordered sequence and work on them as a whole (grouping together related data). Array organize data in such a way that it can be easily sorted.
To create an array, we use a declaration statement. An array declaration should indicate three things:
1. The type of value to be stored in each element.
2. The name of the array.
3. The number of elements in the array.
The basic format of an array declaration is as follows:
Syntax:-
datatype name of the array [Number of elements/Size of array];
For Example:-
Int temperature[7];
Where-
Int- type/datatype of each element.
Temperature- Name of the array.
[7]- Size of array or Number of element in array.
Int- type/datatype of each element.
Temperature- Name of the array.
[7]- Size of array or Number of element in array.
Also Read: Structure Of C Language Program .
To access an element in an array, We use square brackets( [ ] ) after the array name specify the index of the element to be accessed.
array name [index Number]
Sample Code:
#Sample code of an array
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int a[10]; //array created
int i; clrscr();
printf("enter 10 rollno's:\n");
for(i=0; i<=9; i=i+1)
{
scanf("%d",7a[i]);
}
printf("the data is\n");
for(i=0; i<=9; i=i+1)
{
printf("%d ",a[i]);
}
getch();
}
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int a[10]; //array created
int i; clrscr();
printf("enter 10 rollno's:\n");
for(i=0; i<=9; i=i+1)
{
scanf("%d",7a[i]);
}
printf("the data is\n");
for(i=0; i<=9; i=i+1)
{
printf("%d ",a[i]);
}
getch();
}
* Initializing element of an array at the time of creation.
We can initialize the values of the individual array element at the time of declaring/creating an array. The is done by declaring the values after the array declaration. The values are enclosed in a block and are separated by a comma.
Syntax:- datatype name of the array [size]={...values...};
The number of values should not exceed the size of the array.
Also Read: Variables & Datatypes In C Language .
For example:-.
Also Read: Variables & Datatypes In C Language .
For example:-.
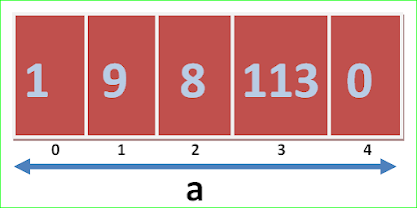
int x[5]={1,9,8,113,0};
Will create an array and also initialize/fill its elements at the time of creation.
If we initialize elements of an array at the time of declaration/creation, then we can even leave the [ ] (square brackets) after the array name empty.
For Example:-
int x[ ]={0,4,7,-6,13};
In such a case, the size of the array will depend on the number of values in the blocks. The size will be automatically determine by compiler.
Sample Code:
//Program to Initialize elements of an array at the time of creation.
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int i;
int a[7]={ 5,6,3,6,8,9,11,13 };
clrscr();
printf("The data is\n");
for( i=0; i<=6; i=i+1)
{
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
getch();
}
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int i;
int a[7]={ 5,6,3,6,8,9,11,13 };
clrscr();
printf("The data is\n");
for( i=0; i<=6; i=i+1)
{
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
getch();
}
* Types of array
| A. One Dimensional | B. Multi Dimensional |
One Dimensional array
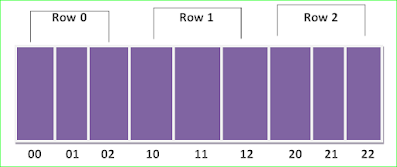
One dimensions array is a list of related variable. 1d array are also called Vectors in mathematics. While creating a one dimensional array, a single square bracket ([ ]) is used/specified after the variable/array name.
Syntax:- datatype array name [size];
Multi Dimensional array
A Multidimensional array is an they has two or more dimensions, and an individual element is Access through the combination of two or more indices/square brackets.
Syntax:- array name[r][c];
Where, r= total number of rows
c=total number of columns
Array can be used to represent multidimensional data, Just like, a chess board or a checker board. An array can have any number of dimensions. Multidimensional array are used for tables and other complex arrangements.
Also Read: Format Specifier In C Programming .
A multidimensional array is an array of array. There is no limit, in principle, to the number of indices which an array can have.
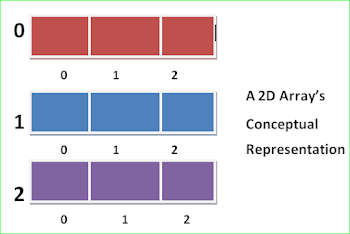
The simplest form of multidimensional array is the two dimensional. In a two dimensional array, The location of any specific element is specified by two indices. If you think of a two dimensional array as a table of information, one index indicates the row, the other indicates the column.
Creating A Two Dimension Array
Syntax:- datatype name of the array[r][c];
Where, datatype= Any valid datatype
r= total number of rows
c= total number of columns
For Example:-
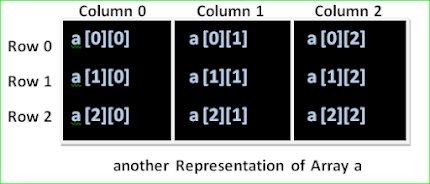
int a[3][3];
The array a has 3 rows and 3 columns. Both rows and columns are indexed from 0.
To access any element in a two dimensional array, we need two indicates to pin-point it- one for the row, and one for the column.
array name [rows no.] [column no.]
For example:-
To access the 2nd element in the first row of array a, we will use:
a [0][1]
Although we can visualize two dimensional arrays as tables, that not the way they are actually stored in computer memory. C stores array in row-major order, with row 0 first, then row1, and so forth.
Initializing two dimensional array
Multidimensional arrays can be initialized by specifying bracketed values for each row.
For Example:-
Int x[2][4]={ {5,6,4,10} //data of 1st row
{3,5,-6,-9} }; //data of 2nd row
We can also initialize a two dimensional array by providing the initial values in one sequence inside a curly braces, Omitting the inner braces(used to represent individual rows).
Also Read: Control Statements In C - language .
For Example:-
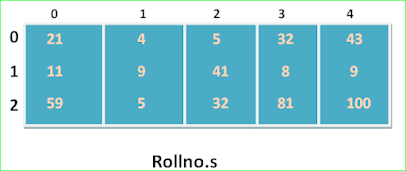
int rollno.s [3][5]={21,,4,5,32,
43,11,9,41,8,9,
59,5,32,81,100 };
/*once the compiler has seen enough values to fill 1 row it begins filling the next*/
Accessing elements of a two dimensional array
Nested for loop are ideal for processing multidimensional arrays. A pair of nested for loops - one that steps through every row index and one that steps through each column index.
Sample Code:
//Program of Accesing A 2d Array.
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int i,j; // i- For rows and j- For Columns
int a[3][3];
clrscr();
printf("Enter 9 values\n");
for( i=0; i<=2; i=i+1 )
{
for( j=0; j<=2; j=j+1 )
{
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
}
}
printf("The data is\n");
for( i=0; i<=2; j=j+1)
{
for( j=0; j<=2; j=j+1)
{
printf("%d ",a[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
getch();
}
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int i,j; // i- For rows and j- For Columns
int a[3][3];
clrscr();
printf("Enter 9 values\n");
for( i=0; i<=2; i=i+1 )
{
for( j=0; j<=2; j=j+1 )
{
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
}
}
printf("The data is\n");
for( i=0; i<=2; j=j+1)
{
for( j=0; j<=2; j=j+1)
{
printf("%d ",a[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
getch();
}
We will going on series of C Programming language of all topics. So, you can follow us for more updates.






Comments
Post a Comment